STOP-MATING
Novel Strategies to Disrupt Mosquito Mating for Vector Control
About the Project
STOP-MATING is a European research initiative

STOP-MATING is a European research initiative
Funded under the MSCA Staff Exchange programme (HORIZON-MSCA-2023-SE-01), STOP-MATING starts in 2024 to bring together interdisciplinary experts to design novel vector control approaches to disrupt the mating behaviour of disease-transmitting mosquitoes. Our aim is to understand the molecular and neurobiological mechanisms underlying mosquito mating and to develop novel tools to target this mechanism and reduce mosquito population numbers. Our interdisciplinary consortium bridges research in bioinformatics, neuroscience, biophysics, biotechnology, field ecology and vector control to address the emergent challenge of mosquito-borne disease geographical expansion. Our goal is to both provide basic biology knowledge and develop novel vector control tools.
About the Project
STOP-MATING is a European research initiative
Funded under the MSCA Staff Exchange programme (HORIZON-MSCA-2023-SE-01), STOP-MATING starts in 2024 to bring together interdisciplinary experts to design novel vector control approaches to disrupt the mating behaviour of disease-transmitting mosquitoes. Our aim is to understand the molecular and neurobiological mechanisms underlying mosquito mating and to develop novel tools to target this mechanism and reduce mosquito population numbers. Our interdisciplinary consortium bridges research in bioinformatics, neuroscience, biophysics, biotechnology, field ecology and vector control to address the emergent challenge of mosquito-borne disease geographical expansion. Our goal is to both provide basic biology knowledge and develop novel vector control tools.

Objectives
Develop standardized protocols and assays to study mosquito mating and related behaviours both in the lab and the field
Develop gene knockouts and analyze changes in mating behaviour in key mosquito species
Identify molecular and neurological targets involved in mosquito mating
Improve our understanding of mosquito mating behaviour in natural settings.
Translate discoveries into innovative tools to stop mosquito reproduction (e.g., acoustic lures, gene drives, mating disruptors).
Promote staff exchange, capacity building and knowledge transfer across institutions.
Validate biological targets across mosquito species and environments through international fieldwork.
Vision & Values
Our vision is to reduce the global burden of mosquito-borne diseases through targeted disruption of mosquito mating behaviour, by combining cutting-edge research with responsible innovation.
We believe that excellence in science must go hand in hand with inclusiveness, ethics, and long-term impact. Our work is rooted in real-world needs and is shaped by collaboration between European and African institutions, academic and industrial sectors, and multiple scientific disciplines.
Core values
Scientific excellence and research integrity aligned with European standards
Ethical responsibility, including respect for biodiversity and fundamental rights
Gender equality and support for women scientists in all regions
Global equity and collaboration between Europe and Africa
Open science, data sharing, and reproducibility
Sustainability through long-term capacity building and researcher training
Scientific Approach
STOP-MATING combines bioinformatics, wet lab and field-based research to understand and disrupt mosquito mating behaviour. Our scientific strategy includes:
Scientific Approach
STOP-MATING combines bioinformatics, wet lab and field-based research to understand and disrupt mosquito mating behaviour. Our scientific strategy includes:

Bioinformatics analysis to identify candidate genes involved in mosquito mating behaviour
Transcriptomics and CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing to uncover and manipulate mating-related genes
Auditory and behavioural tests to study the neurobiological basis of mosquito mating behaviour
Ecological studies in Madagascar and the Central African Republic to improve our understanding of mating behaviour in natural malaria mosquito populations
Field-deployable solutions to disrupt mosquito mating such as acoustic lures, mating disruptors and gene drive technologies

Bioinformatics analysis to identify candidate genes involved in mosquito mating behaviour
Transcriptomics and CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing to uncover and manipulate mating-related genes
Auditory and behavioural tests to study the neurobiological basis of mosquito mating behaviour
Ecological studies in Madagascar and the Central African Republic to improve our understanding of mating behaviour in natural malaria mosquito populations
Field-deployable solutions to disrupt mosquito mating such as acoustic lures, mating disruptors and gene drive technologies
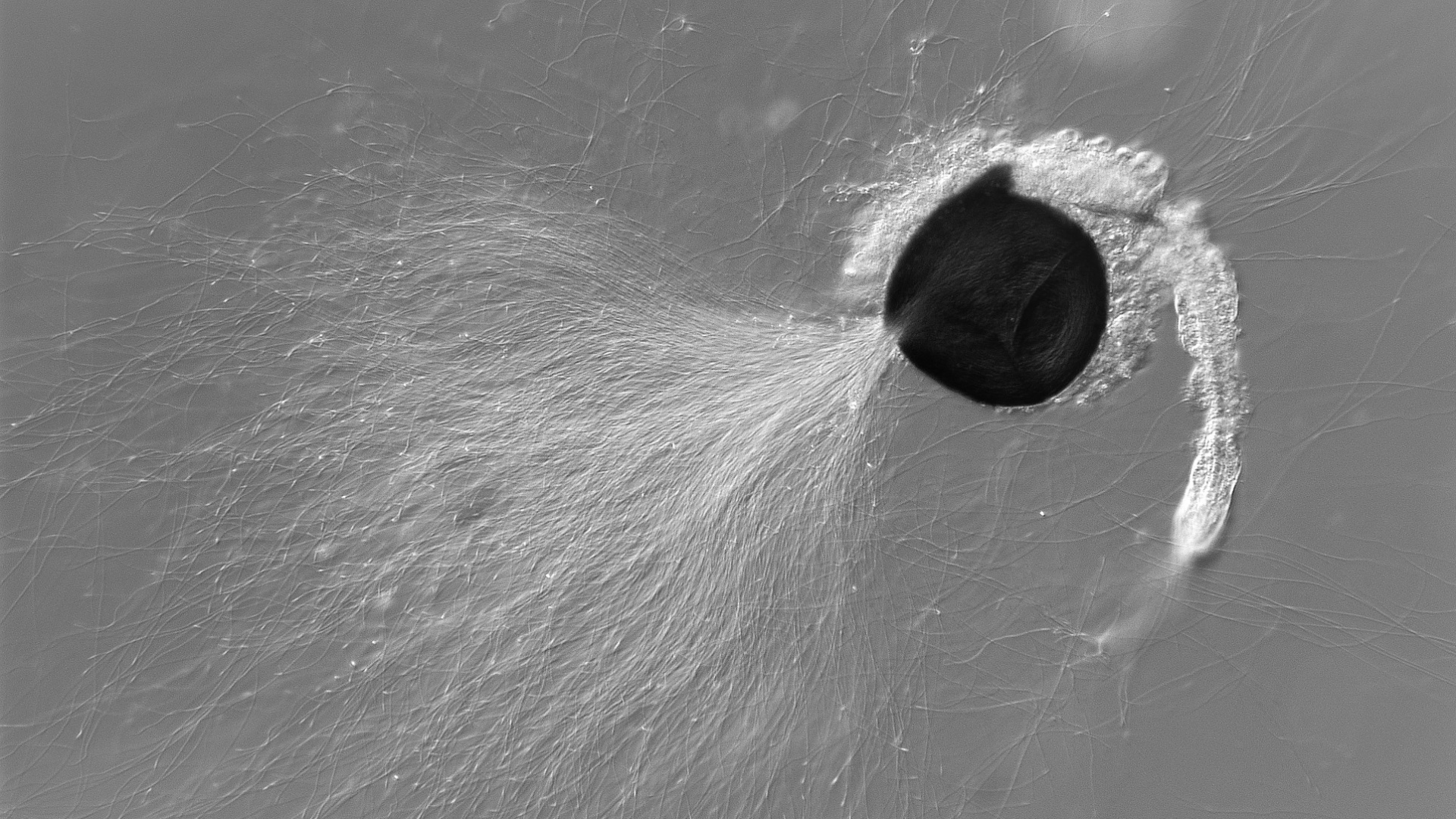

Governance
- Project Coordinator (CSIC): Oversees execution, timelines, and reporting.
- Work Package Leaders: Manage the scientific delivery and internal coordination.
- Secondment Hosts: Facilitate researcher mobility, integration, and supervision.
- Project Board: Decision-making body composed of WP leads and the coordinator.
Secondments
Secondments are the heart of STOP-MATING. Researchers are exchanged between institutions to foster international, intersectoral and interdisciplinary collaboration, in line with the goals of the MSCA Staff Exchange scheme.
These mobility experiences promote knowledge sharing, hands-on learning, and strong cooperation between scientific and technical teams in Europe and Africa. Key features:
Secondments
Secondments are the heart of STOP-MATING. Researchers are exchanged between institutions to foster international, intersectoral and interdisciplinary collaboration, in line with the goals of the MSCA Staff Exchange scheme.
These mobility experiences promote knowledge sharing, hands-on learning, and strong cooperation between scientific and technical teams in Europe and Africa. Key features:
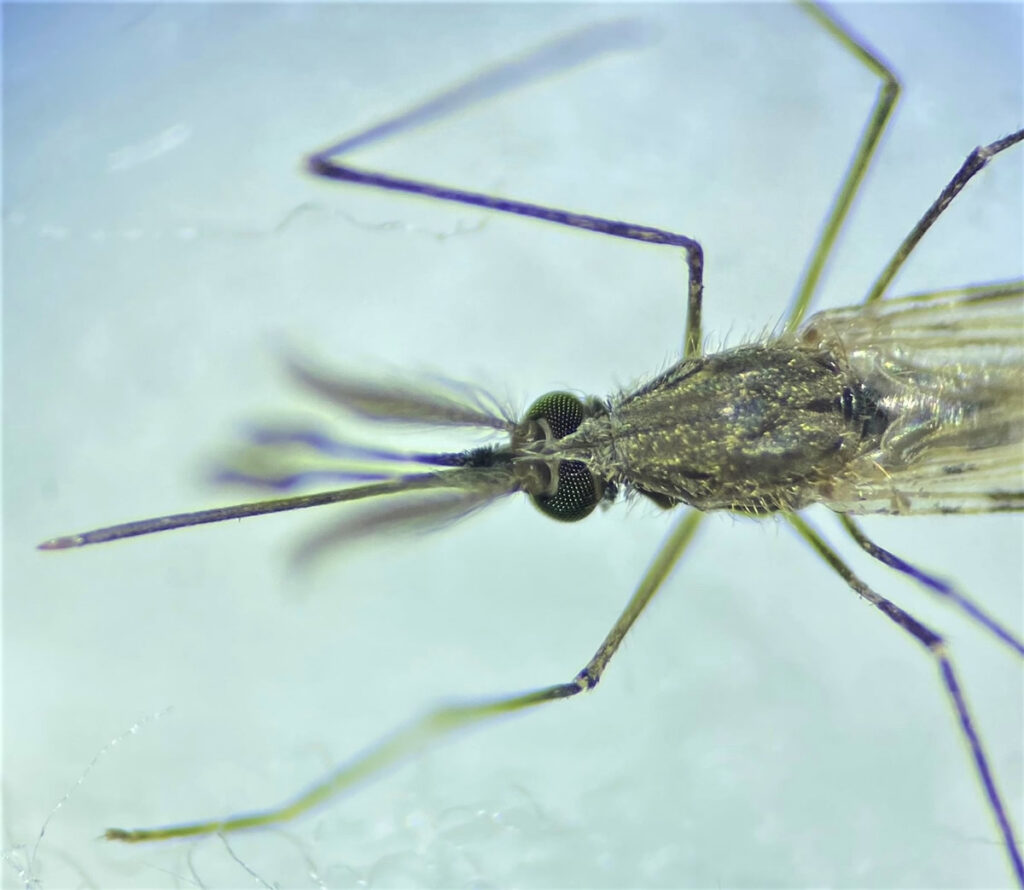

Bilateral or multilateral staff exchange across European and African partners.
Intersectoral exchanges including academic organisations and industrial partners.
Mobility plans aligned with research tasks in each WP.
Capacity building through real-time lab/field collaboration.
Mobility monitoring and best practices based on MSCA Staff Exchange guidelines.

Dissemination & Impact
We aim to raise awareness, communicate results, and create long-term value. Our strategy targets the scientific community, industry stakeholders, and the general public, especially those communities affected by mosquito-borne diseases.
- Open access publications and conference participation.
- Training sessions in bioinformatics.
- Engagement via public events and educational material.
- Tools and results shared to strengthen our understanding of mosquito mating behaviour, and to contribute with innovative vector control solutions.
Work Packages
Bioinformatic analysis
Gene knockout generation
Phenotypic characterization using behavioural assays
Bioinformatic analysis in relevant mosquito species
Gene knockout generation in relevant mosquito species
Phenotypic testing
Design of acoustic trapping systems
Development of hit compounds with potential to interfere with mosquito mating behaviour
Generation of gene drive systems targeting mosquito mating
Coordination of intersectoral secondments and hosting schemes
Organisation of training events (wet-lab, bioinformatics, fieldwork)
Outreach activities (e.g., Researchers' Night, school visits)
Day-to-day management of the project and support to partners
Monitoring of milestones, deliverables, and secondment flows
Coordination of meetings, ethics reviews, and advisory inputs

